Introduction
In today’s fast digital landscape, the adoption of a multi-cloud strategy is gaining increasing popularity. This strategy involves utilizing cloud services from a variety of public cloud providers to cater to similar IT solutions or workloads. However, Gartner emphasizes that a multi-cloud strategy can escalate management and governance challenges, complexity, and IT costs, while also demanding a higher level of skills. Despite these challenges, when effectively managed, a multi-cloud strategy can significantly enhance access to a broad spectrum of technological options and innovative, best-of-breed capabilities.
Furthermore, in this blog we will come across cross-platform data management, which is crucial for ensuring seamless integration and interoperability across these diverse cloud environments. Additionally, we will explore the use case and challenges of multi-cloud cross-platform data management.
Understanding Multi-Cloud Environment & Data Management
Multi-cloud data management involves distributing data across multiple cloud environments to enhance performance, resilience, and leverage specific cloud features. It’s a strategic approach for businesses to diversify and optimize their cloud resources, moving away from reliance on a single provider. This diversification is crucial for several reasons:
Firstly, it liberates businesses from vendor lock-ins, offering greater flexibility in choosing and scaling cloud services that best suit their needs, whether for computational power, storage solutions, or specialized services.
Another key benefit is risk mitigation. By spreading data and processes across multiple cloud platforms, companies reduce the impact of potential downtime or failures in any one provider, thereby ensuring more robust operational continuity and resilience against unexpected disruptions.
Key capabilities for successful multi-cloud data management encompass:
- Data Discovery: Identifying data across diverse cloud environments.
- Data Lineage: Tracking data origins and usage patterns.
- Data Migration: Transferring data seamlessly between cloud platforms.
- Data Security: Safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access.
- Access Management: Managing permissions and policies for controlled data access.
- Data Governance: Ensuring compliance with regulations and internal policies.
- Performance Management: Monitoring and enhancing data processing efficiency.
- Cost Optimization: Managing expenses by optimizing resource usage and limits.
Multicloud Data Management Challenges and Use-Cases
Data portability remains a critical challenge for enterprises operating in multi-cloud environments. Each major cloud provider uses proprietary APIs for data management, complicating seamless data sharing between clouds and often leading to data silos. Even organizations utilizing open-source technologies struggle to transfer large datasets between cloud providers efficiently.
– Use case: Unified Cross-Cloud Portability: To address the above challenges, enterprises can leverage cross-cloud data sharing technologies like Microsoft Azure Arc–enabled data services, which provide cohesive data management across on-premises, multicloud, and edge environments, ensuring greater security and consistency.
– Additionally, platforms such as Amazon EKS Anywhere facilitate application deployment across diverse cloud environments, enhancing data and application portability. These solutions enable smoother transitions and better integration across different cloud providers, addressing the challenges of data silos and improving operational efficiency.
Unstructured and Diverse Data in the CloudModern enterprises face the challenge of managing diverse data types such as transactional logs and security information across multiple cloud deployments. This distributed data landscape hampers holistic analysis and decision-making.
– Use case: Centralized Data Repository Optimization: To optimize data utilization, enterprises need to consolidate their data into centralized repositories such as Microsoft Azure Data Lake Storage. This approach not only ensures secure data storage but also enables comprehensive analysis, leveraging platforms like Azure Blob Storage for scalable and cost-effective data management. By centralizing data, organizations can extract valuable insights to drive operational efficiencies and informed decision-making.
Multiple Cloud Security Issues Across Cloud ProvidersDeploying applications and databases across multiple public clouds increases the attack surface and exposes organizations to diverse cyber threats. While some advocate for multi-cloud setups to mitigate risks, breaches in one cloud can potentially propagate to others within the environment.
– Use case: Enhanced Security for Multi-Cloud Deployments: Microsoft Defender for Cloud addresses the above challenges by providing unified security management with DevSecOps, continuous monitoring and actionable recommendations through Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM), and specific protections for servers, containers, storage, and databases via its Cloud Workload Protection Platform (CWPP). This comprehensive approach ensures a secure and resilient multi-cloud environment.
Disaster Recovery may not be the only solutionTraditional disaster recovery strategies confined within single cloud environments such as AWS or Azure have historically offered stability but also exposed vulnerabilities specific to regions.
– Use case: Implementing cross-cloud disaster recovery: Implementing cross-cloud disaster recovery addresses the limitations of traditional single-cloud approaches like AWS or Azure by leveraging multiple cloud providers simultaneously. This strategy enhances resilience by distributing operations across diverse regions and platforms, thereby minimizing single points of failure and ensuring business continuity.
Customers and partners utilizing VMware Cloud on AWS and Azure VMware Solution can deploy VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM), a VMware-integrated solution that automates disaster recovery orchestration and enables non-disruptive testing of recovery plans. This approach ensures readiness and reliability across hybrid cloud environments, safeguarding against potential disruptions effectively.
Data Retention and legal compliance issuesManaging data retention in multi-cloud environments requires organizations to navigate legal and operational requirements effectively. Conducting comprehensive data inventories helps identify data subject to regulatory compliance and operational needs. Establishing robust data retention policies ensures secure and cost-effective storage of critical data over specified durations.
– Use Case: Leveraging Microsoft® Blob Storage for Data Retention:
Companies can utilize Microsoft® Blob Storage to manage data retention effectively. Microsoft® guarantees that your data remains under your exclusive control at all times. Whether data is deleted via API or due to subscription changes, Microsoft® applies specific policies that dictate how long data can be retained for potential recovery purposes. This ensures organizations can securely manage and retrieve critical data while meeting regulatory and operational requirements effectively.
Cross Cloud Data Sharing: The Best Strategy to Resolve Multi-cloud Data Management Challenges
Cross-cloud means being able to run applications and workloads smoothly across different cloud providers. It came about with the rise of multi-cloud strategies, where organizations use various public, private, and edge clouds along with on-premises setups. Cross-cloud ensures that everything from applications to security measures can work consistently across different cloud providers and on-site systems. This standardization helps organizations manage their operations more effectively across diverse cloud environments.
The concept of cross-cloud solutions offers a promising approach to overcoming the challenges mentioned above in the blog. These solutions are designed to bridge the gaps between cloud silos and enhance data portability across different cloud environments. Key components of cross-cloud strategies include:
- Cloud-Agnostic Data Management Platforms: These platforms unify data management capabilities across various cloud providers, ensuring consistent functionalities and enabling cost-effective data sharing. They provide organizations with the ability to manage data uniformly regardless of where it resides within multi-cloud infrastructures.
- High-Throughput Communication Infrastructure: To facilitate seamless data movement across regions and clouds, robust communication infrastructures are essential. These infrastructures enable organizations to achieve complete data portability, ensuring that data can be accessed and utilized anywhere in the world, irrespective of its physical location.
Implementing cross-cloud strategies brings several benefits to organizations:
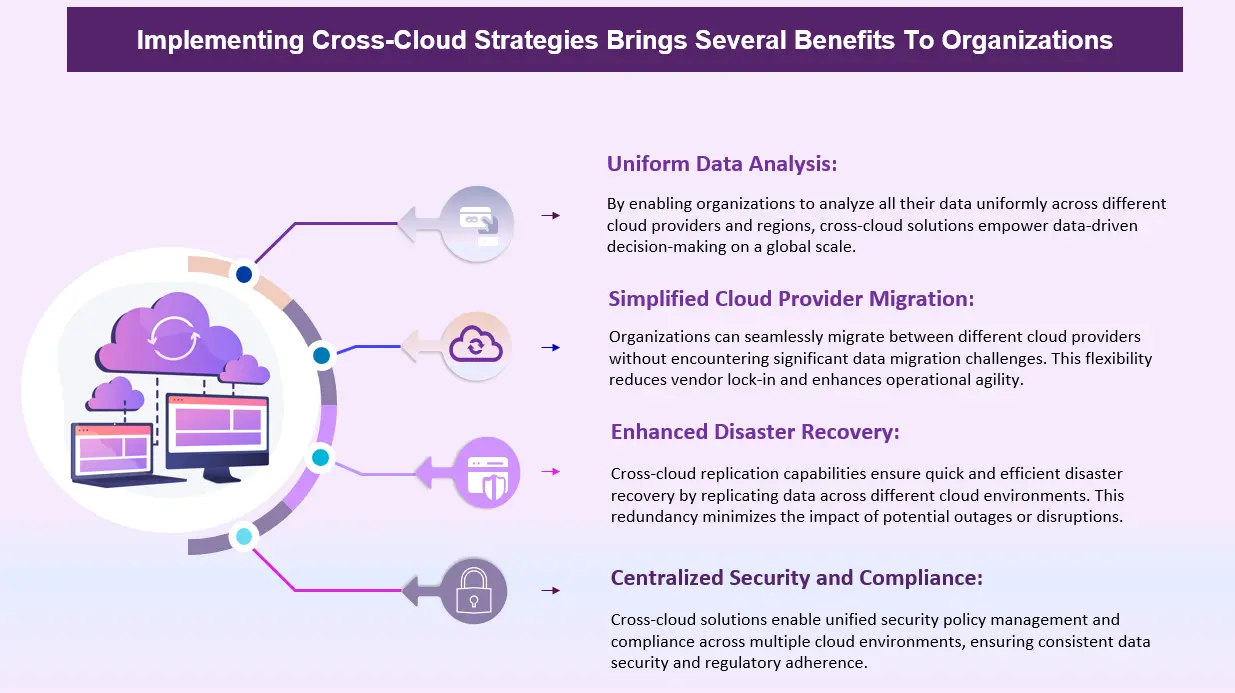
In summary, adopting cross-cloud strategies allows organizations to break down data silos, improve operational efficiency, and leverage data more effectively to drive innovation and competitive advantage in today’s interconnected digital landscape.
Conclusion
In navigating today’s digital landscape, the adoption of a multi-cloud strategy presents both opportunities and challenges for organizations seeking to optimize their IT operations. Addressing challenges such as data portability, security standardization, disaster recovery, and regulatory compliance requires robust solutions like cross-cloud data sharing technologies. These technologies facilitate seamless data integration and interoperability across diverse cloud environments, enabling organizations to harness the full potential of their cloud investments.
By embracing cross-cloud strategies, businesses can achieve unified data management, enhance operational efficiencies, and maintain competitive agility in an increasingly interconnected world.



