Introduction
In the fast-evolving realm of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning, efficient data processing is crucial. Choosing the right networking technology is key to meeting AI’s demanding requirements for high throughput, low latency, scalability, and reliability. InfiniBand and Ethernet are prominent contenders in this field, each tailored to different aspects of AI networking.
InfiniBand is renowned for its high-speed capabilities, initially developed for supercomputers. It offers ultra-high bandwidth and minimal latency, ideal for real-time AI tasks like autonomous vehicles and high-frequency trading. Ethernet, originally a LAN technology, has adapted to become versatile for cloud and enterprise networks, prioritizing scalability and cost-effectiveness.
This article compares InfiniBand and Ethernet, highlighting their strengths and applications in AI networking. Understanding these technologies helps businesses optimize their AI infrastructure, gaining a competitive edge in today’s AI-driven industries.
Understanding High Speed Interconnects AI Networking Options
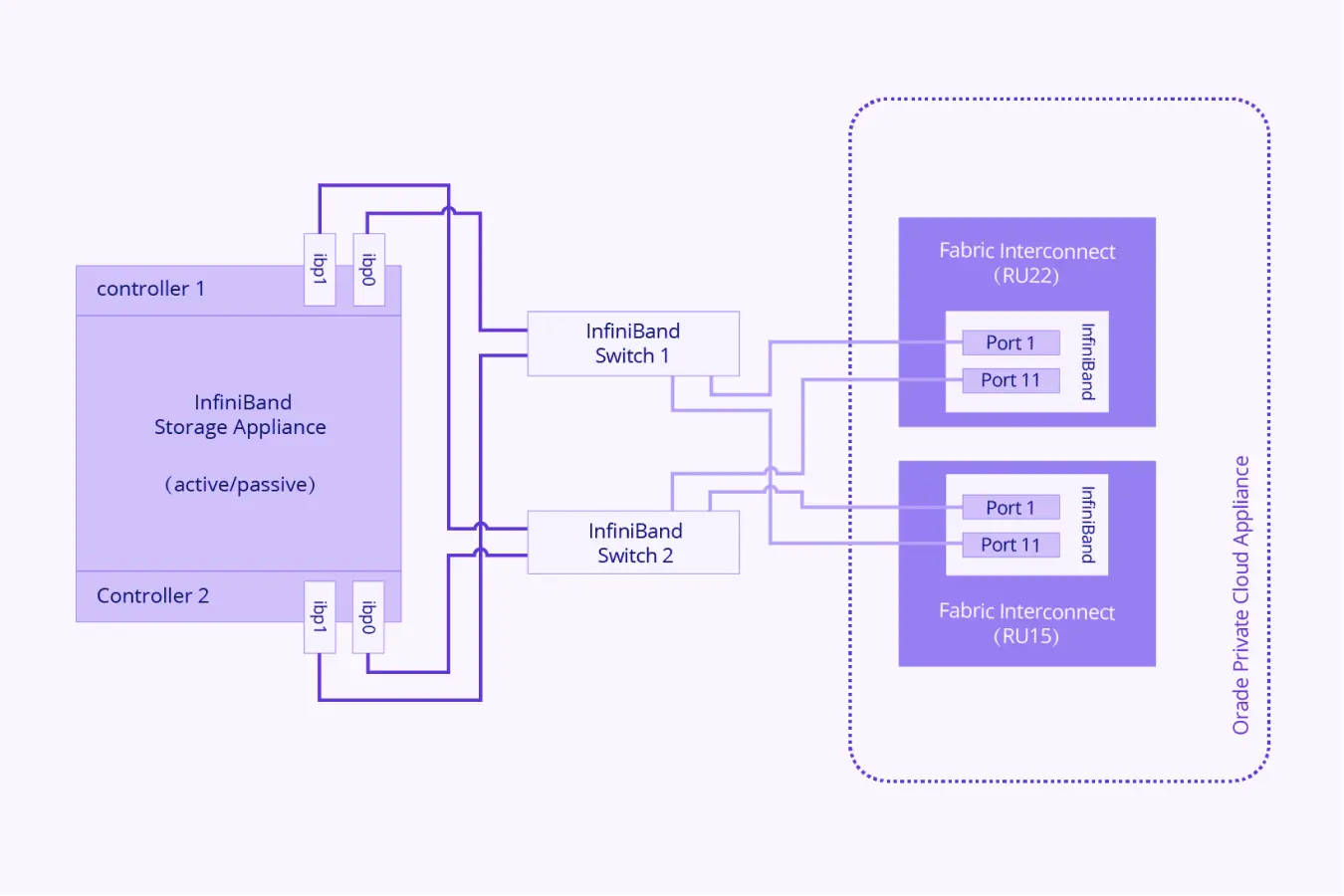
- InfiniBand: InfiniBand and Ethernet networks differ significantly in their design and intended use. InfiniBand serves as a high-speed network technology widely adopted in supercomputer clusters for its reliability, low latency, and high bandwidth capabilities. It’s particularly favored for connecting GPU servers, crucial for high-performance computing tasks.
The InfiniBand standard supports data rates like Single Data Rate (SDR), Double Data Rate (DDR), and Quadruple Data Rate (QDR), enabling transmission speeds up to 120Gbits/sec over 12X cables. This makes it ideal for environments requiring fast and efficient data processing.
- Ethernet: Ethernet, in contrast, has been the dominant communication protocol in LAN environments since its inception in 1980. It focuses on facilitating easy information flow between multiple systems with an emphasis on distribution and compatibility. Initially relying on TCP/IP, Ethernet has evolved to include technologies like RoCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet).
Ethernet networks are commonly used to connect computers, printers, scanners, and other devices within local area networks. They support various types including Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet, and 10 Gigabit Ethernet, offering flexibility for both wired and wireless network configurations.
InfiniBand vs Ethernet for AI Networking
| Feature |
InfiniBand |
Ethernet |
| Bandwidth |
InfiniBand offers high bandwidth, typically ranging from hundreds to thousands of Gbps.
The latest standards support speeds up to 400 Gbps.
|
Ethernet bandwidth has also evolved significantly, reaching up to 100 Gbps in recent standards.
However, it generally offers lower bandwidth compared to InfiniBand in equivalent setups.
|
| Latency |
InfiniBand is known for its low-latency characteristics, delivering sub-microsecond latency.
This makes it ideal for applications where minimizing communication delays is critical, such as high-frequency trading and real-time AI inference.
|
Ethernet traditionally has higher latency compared to InfiniBand, although advancements in Ethernet standards have reduced latency significantly.
It is suitable for many AI applications but may not meet the ultra-low latency requirements of certain high-performance scenarios.
|
| Packet Loss |
InfiniBand typically experiences lower packet loss rates compared to Ethernet, ensuring more reliable data transmission in large-scale, high-throughput environments like AI clusters and supercomputing centers. |
Ethernet networks can experience higher packet loss rates under heavy traffic conditions, although improvements in network management and quality of service (QoS) have mitigated this issue to some extent. |
| Data Transmission Reliability |
InfiniBand offers highly reliable data transmission with minimal packet loss, critical for maintaining data integrity and reducing the need for retransmissions.
This reliability is beneficial in AI environments handling massive datasets and sensitive real-time computations.
|
Ethernet networks provide reliable data transmission capabilities, although they may encounter occasional packet loss, particularly in congested network scenarios. |
| Network Performance |
InfiniBand provides superior network performance suited for AI workloads that demand rapid data processing and low-latency communication. Its high-speed interconnects optimize throughput and minimize latency, enhancing overall system performance in HPC and AI-driven applications. |
Ethernet continues to evolve with advancements in speed and efficiency, offering competitive network performance suitable for a broad range of AI applications, from cloud-based services to enterprise data centers. |
| Scalability |
InfiniBand excels in scalability, particularly for large clusters and high-performance computing environments.
It supports thousands of nodes efficiently, making it ideal for massive AI deployments requiring seamless communication across distributed systems.
|
Ethernet is also scalable and widely used in cloud environments and medium-sized data centers.
While it may face limitations in very large clusters compared to InfiniBand, innovations like Ethernet fabrics enhance scalability for expanding AI workloads.
|
| CPU Overhead |
InfiniBand imposes lower CPU overhead compared to Ethernet, optimizing computational resources for AI tasks rather than network management.
This efficiency is crucial for maximizing processing power and reducing latency in AI workflows.
|
Ethernet networks may incur higher CPU overhead due to protocol processing and software-defined networking (SDN) overheads, although advancements in hardware offload capabilities mitigate these impacts, improving overall system efficiency.
|
| Cost |
InfiniBand infrastructure typically involves higher initial costs per port compared to Ethernet solutions.
However, organizations must consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), factoring in performance gains and operational efficiencies achieved with InfiniBand’s high-speed, low-latency capabilities.
|
Ethernet offers a more cost-effective solution with lower initial deployment costs and affordable hardware options.
It remains a preferred choice for budget-conscious AI implementations without compromising scalability and network performance.
|
|
Choosing the Right Technology for Your AI Networking Needs
Conclusion
Choosing between InfiniBand and Ethernet for AI networking depends on specific requirements such as performance demands, budget constraints, scalability needs, and the criticality of data transmission reliability. While InfiniBand excels in high-performance environments demanding ultra-low latency and high bandwidth, Ethernet offers a cost-effective and scalable solution suitable for a wide range of AI applications. Evaluate your infrastructure’s needs carefully to determine which technology aligns best with your AI networking goals. By understanding these differences, organizations can make informed decisions to support their AI initiatives effectively and efficiently.